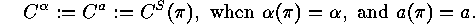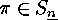 will be denoted by
will be denoted by 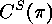 ,
the centralizer by
,
the centralizer by 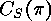 , so that we obtain the following descriptions
and properties of conjugacy classes and centralizers of elements of
, so that we obtain the following descriptions
and properties of conjugacy classes and centralizers of elements of 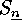 :
:
The conjugacy class of 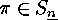 will be denoted by
will be denoted by 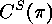 ,
the centralizer by
,
the centralizer by 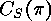 , so that we obtain the following descriptions
and properties of conjugacy classes and centralizers of elements of
, so that we obtain the following descriptions
and properties of conjugacy classes and centralizers of elements of 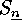 :
:
There are some examples to compute the orders of the
conjugacy classes and centralizers
in 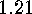 .
. Corollary
Let
Corollary
Let 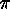 and
and 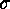 denote elements of
denote elements of 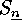 . Then
. Then
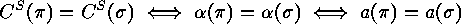 .
.
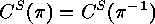 , i.e.
, i.e. 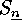 is ambivalent
, which means that each element is a conjugate of its
inverse.
is ambivalent
, which means that each element is a conjugate of its
inverse.
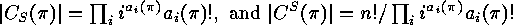 .
.
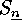 .
.
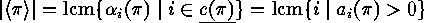 .
.
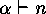 occurs as the cycle
partition
of some
occurs as the cycle
partition
of some 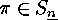 .
.
(The first, second, fourth and fifth item is clear from the foregoing, while the
third one follows from the fact that there are exactly 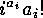 mappings
which map a set of
mappings
which map a set of 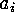
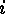 -tuples onto this same set up to cyclic permutations
inside each
-tuples onto this same set up to cyclic permutations
inside each 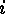 -tuple.)
For the sake of simplicity we can therefore parametrize
the conjugacy classes
of elements in
-tuple.)
For the sake of simplicity we can therefore parametrize
the conjugacy classes
of elements in 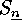 (and correspondingly in
(and correspondingly in 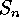 )
by partitions or cycle types putting
)
by partitions or cycle types putting